The buildings sector represents a significant contributor to energy consumption in Europe,
responsible for over a third of the EU’s greenhouse gas emissions. According to the
European Green Deal, decarbonization of the energy sector plays a key role in the
EU’s aspiration for climate neutrality. Alongside cleaner energy sources and
enhanced appliance efficiency, reducing unnecessary energy usage in office spaces
is a viable strategy. This effective and sustainable solution can be achieved by
employing advanced IR occupancy sensors. These sensors not only detect human
presence but also determine occupancy levels, allowing them to intelligently adjust
lighting and HVAC systems as needed. By turning off lights and optimizing
temperature settings when an area is partially occupied or unoccupied, IR
occupancy sensors significantly contribute to energy savings. This technology not
only is intended to reduce operational costs but also aims to lower a building’s
carbon footprint. Moreover, it enhances the overall workplace experience by
providing a comfortable and well-lit environment while minimizing energy waste. In
an era where environmental consciousness and cost-efficiency are paramount, IR
occupancy sensors are poised to become an indispensable tool for modern office
spaces.
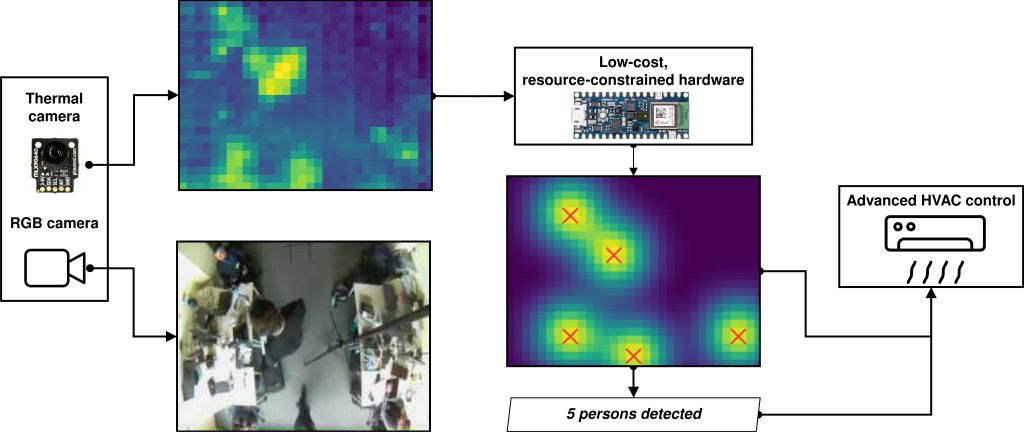
The IR occupancy sensor employs a low-resolution thermal camera to safeguard the
privacy of office space users. To estimate occupancy count the tailored UNet-like
neural network is applied. Additionally, all computations are performed on the edge
using efficient low-cost hardware limiting the transmission of sensitive data from
sensors. Furthermore, all data processing occurs at the sensor’s edge, using efficient
and low-cost hardware, minimizing the transmission of sensitive data.